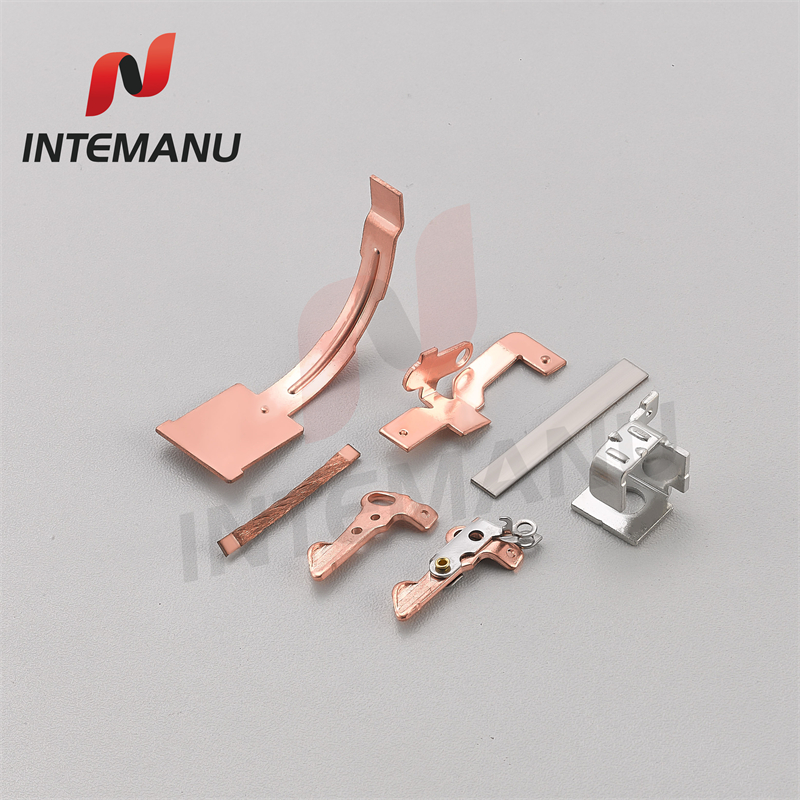
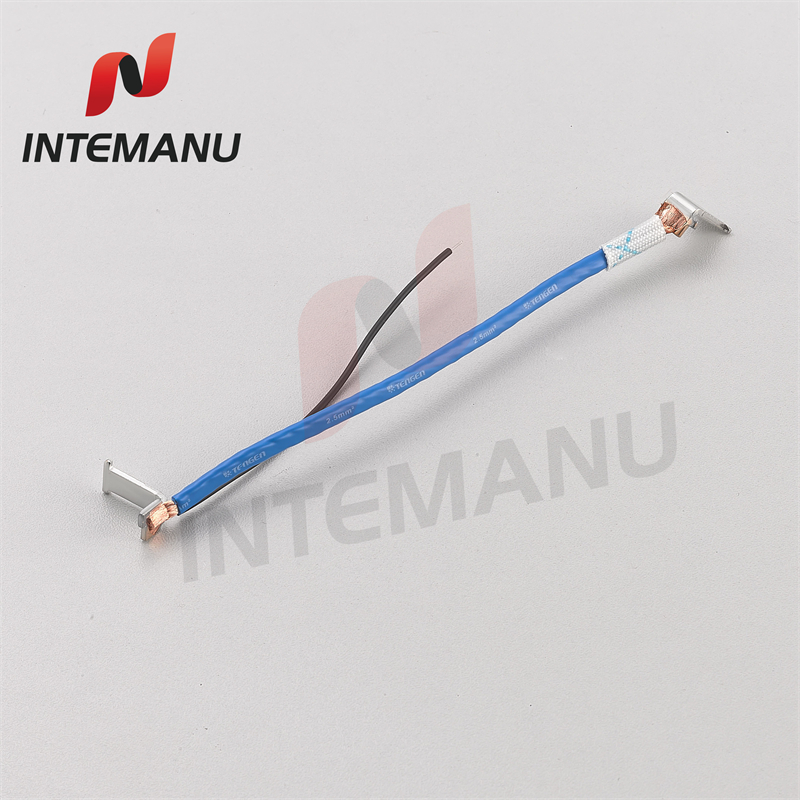
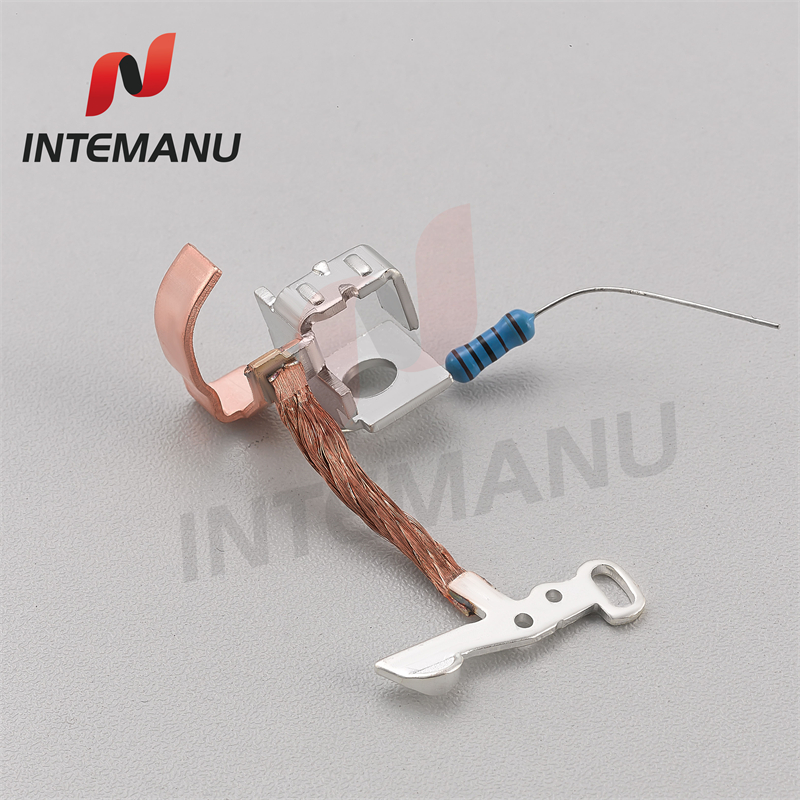
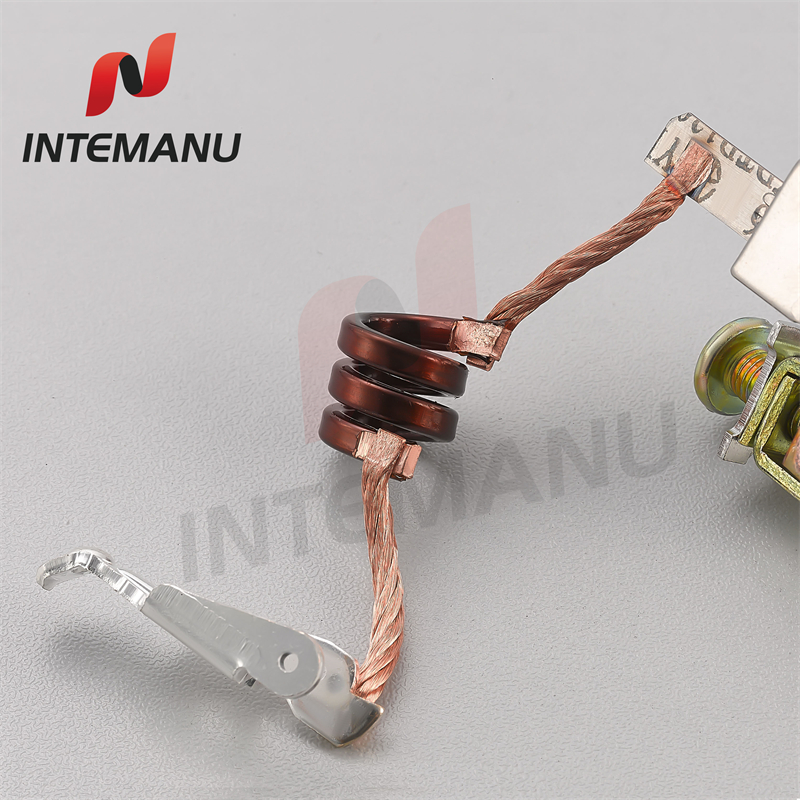
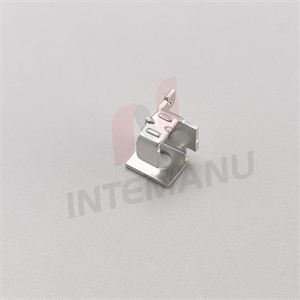
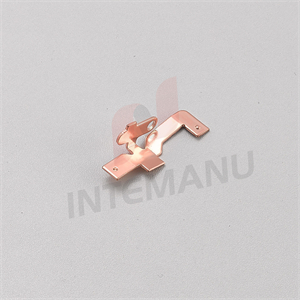
XML7B MCB Circuit Breaker Bimetallic System
XML7B MCB Circuit Breaker Thermal Tripping Mechanism consists of bimetall strip, soft connection, arc runner, braid wire, moving contact and moving contact holder.
The thermal tripping arrangement consists of a bimetallic strip around which a heater coil is wound to create heat depending on the flow of current.
The heater design can be either direct where current is passed through a bimetal strip which affects part of electric circuit or indirect where a coil of current carrying conductor is wound around the bimetallic strip. The deflection of a bimetallic strip activates the tripping mechanism in case of certain overload conditions.
The bimetal strips are made up of two different metals, usually brass and steel. These metals are riveted and welded along their length. These are so designed such that they will not heat the strip to the tripping point for normal currents, but if the current is increased beyond rated value, the strip is warmed, bent and trips the latch. Bimetallic strips are chosen to provide particular time delays under certain overloads.